What do Bitcoins look like? This is one of the concerns that novice crypto enthusiasts ask. This is a genuine question because, as a new user, it is easy to get started with Bitcoin without understanding or even knowing its technical details.
Once you create a Bitcoin wallet, your first Bitcoin wallet will be generated. You can then share it with others so that they can pay you, or others can give you their addresses so that you can transact with them. Bitcoin works the same way as email, only that its address can only be used once.
Even though using BTC is easy, it is important to have enough information about it before you invest your hard-earned money in it.
You need to answer several questions, including; how does Bitcoin look like? What does a real Bitcoin look like? What does a Bitcoin ATM look like? What does a Bitcoin machine look like? What does Bitcoin look like on a computer?
What does a Bitcoin transaction look like? To get answers to these questions and much more, keep reading and become a Bitcoin expert!
What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin might be the most popular cryptocurrency on the planet, but it still remains an enigma to many people.
It is a complicated yet fascinating new-age currency that exists virtually and allows users to be somehow anonymous.
Just like US Dollars or Euros, Bitcoin is designed to pay for goods and services.
You can read this article to know the answer to how many bitcoins are there right now.

Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin has the following features:
Digital
There are no Bitcoin bills or physical Bitcoins. This currency thrives online and can only be tracked by a blockchain.
Within Bitcoin’s blockchain network, there exist constantly growing groups of records that offer a complete history of each transaction. All transactions are posted on a public ledger for everyone to access.
Non Refundable
Once you send traditional or digital currency, there is a way you can dispute the transaction and get your money back. With cryptocurrencies, this is not possible. Once you send BTC to someone, there is no way of getting it back unless the recipient decides to send it back to you.
Fast
The blockchain network in which Bitcoin is built processes payments almost instantaneously.
While normal banks can take days to transfer money, especially for overseas payments, the Bitcoin network only takes a few minutes.
Pseudo-anonymous
Today, banks know everything about their clients. They have a lot of information in their databases, including phone numbers, spending habits, addresses, credit history, and more.
A Bitcoin wallet, on the other hand, is not linked to any personal information. Even though Bitcoin transactions are posted on a public ledger, it is nearly impossible to trace a particular wallet address to a particular person.
You can even decide to make your BTC transactions anonymous by implementing a few steps such as hiding your IP, using a different address for every transaction, and using wallets that prioritize security, ease-of-use, and opaqueness, such as Tezro.
Decentralized
When creating the Bitcoin network, one of Nakamoto’s primary objectives was to create a network that was independent of governing authorities.
It was designed such that every individual, business, or machine involved with mining and/or exchange check becomes part of a vast system.
Additionally, even if part of the system goes down, transactions will keep moving.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
One of the easiest ways of answering the question “what do Bitcoins look like?” is to understand how this digital currency work in the first place. Basically, Bitcoin uses advanced encryption methods to secure and verify transactions.
Every BTC transaction is recorded on a public ledger called a blockchain. This makes it possible for people to trace the transaction history of every coin and stop malevolent individuals from spending coins they don’t own, undo transactions, or make copies.
What Is A Blockchain?
Understanding the blockchain is an integral step towards knowing how Bitcoin works. When you use fiat currency or other traditional payment methods such as credit/debit cards, your transaction history goes through a financial institution.
This institution has to verify and clear every transaction before it is added to your account statement. Normally, this statement is kept and viewed by the bank.
The blockchain in which Bitcoin is built is a revolutionary technology that came to change the transaction history paradigm we have been using for years.
While credit card transactions are stored in the bank and often viewable by the bank and yourself, Bitcoin transactions are stored in nodes.

These nodes can either be servers or computers that are stored in different parts of the world. BTC transactions are transparent and can be viewed by anyone on the network.
In the traditional system, malicious elements within the bank could change records and manipulate clients’ transaction history.
With blockchain, transaction history is free from any foul play. In case anyone modifies their copy of the blockchain, everyone will find out since this copy wouldn’t match other copies in the blockchain.
To protect privacy, users in the BTC blockchain are identified by the following things:
- Wallet addresses- this is a string of random numbers and letters where people can send you BTC. No one can trace a wallet address unless you want them to.
- Transaction amounts.
- Other amounts.
What Does A Bitcoin Transaction Look Like?
From a glance, Bitcoin transactions might seem simple and straightforward. Nonetheless, they are more complex than you might think. What most people, including BTC users, don’t know is that it is almost impossible to send a particular amount of BTC in one go.
When you make a payment, both the Bitcoin wallet and the Bitcoin network have to undergo a set of steps to make sure that the right amount of coins reaches the recipient’s wallet.
It is worth mentioning that Bitcoin is not a single record of a coin. Instead, it is a file with a value that registers as a transaction whenever one initiates a transaction or receipt. There are three main elements involved in every Bitcoin transaction. They include:
- A transaction input: This is the Bitcoin address from which the BTC was sent.
- A transaction output: This is the Bitcoin address to which the BTC was sent.
- The amount.
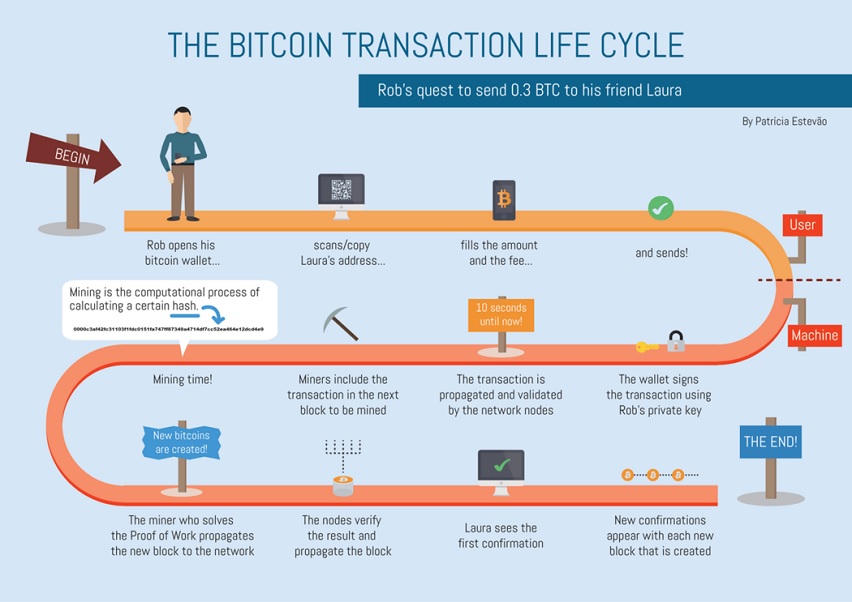
How Does a BTC Transaction Work?
The BTC you send to another person was probably sent to you by someone else. When they were sent to you, the address used was registered on the blockchain network as the transaction input, and your address – the one that was used to send the funds was registered as the transaction output.
When you send BTC to another address, your wallet creates the transaction output, which is basically the address of the party you are sending the coins to.
The transaction will be recorded on the blockchain, with your address as the transaction input.
When that party sends the coins to another party, their address will automatically because the transaction input and the recipient’s address will become the transaction output. The cycle goes on and on…
Using the Bitcoin network, people can trace every transaction way back to when it was first created. It makes it easy for people to know who made a transaction to who and at what time.
This creates a transparent system that cannot be found in traditional payment methods.
First Bitcoin Block
The first block of Bitcoin ever mined is known as the Genesis block. This is the block that forms the foundation of the Bitcoin trading system we know today. It is also the prototype of all other blocks on the BTC blockchain.
The Genesis Block was created in 2009 by Bitcoin’s founder Satoshi Nakamoto, and it set the pace for Bitcoin trading.
Also known as Block 0, the Genesis Block is the ancestor that every Bitcoin block cab trace its lineage back to. Nakamoto mined this block using a CPU, as opposed to the specialized graphic card miners needed today.
It was easy for him to achieve this with a simple CPU because no one knew Bitcoin existed, and it was not worth anything. This is the block that kick-started the process of trading BTC.
Unlike other 500,000+ Bitcoin blocks that came after it, Nakamoto left this message on the code of the block:
“The Times 03/Jan/2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.”
This was taken from the headline of a London Times post dated Jan 3, 2009, that outlined banks being bailed out by the government.
Even though Nakamoto didn’t explain his message, Bitcoin experts interpreted it as a reference to his main objective of developing Bitcoin: To eliminate middlemen and banks that he deemed unreliable and corrupt and create a people-driven currency.
The origin of the Genesis Block is shrouded in mystery as the Bitcoin founder himself, with questions and concerns arising about why the 50 Bitcoins in this block cannot be spent, why the subsequent block took 6 days to mine, and why BTC traders still transfer Bitcoin into the Genesis block.

How Does Bitcoin Wallet Address Look Like?
A Bitcoin wallet is software in which Bitcoins are stored. Bitcoin wallets facilitate the sending and receiving of coins and give ownership of the BTC balance to the user. There are four main types of Bitcoin wallets. They include:
Desktop Wallets
These are wallets installed on the desktop computer and provide the user with complete control of the wallet. They function as an address for the user to send and receive BTC.
Mobile Wallets
These wallets work the same way as desktop wallets. However, they are installed on mobile devices.
Many mobile wallets have dedicated applications for Android and iOS, like Tezro for example.
Tezro allows you to exchange and store crypto assets with total discretion and privacy. Read more here.
Before installing mobile wallets, you need to know that there is significant malware posing as reliable and affordable wallets. It is highly recommended that you research your options before you decide on the one to use.
Web Wallets
These are wallets that can be accessed on any browser or mobile device. You must choose a web wallet carefully since it will store your private keys online.
Hardware Wallets
These are regarded as the most secure Bitcoin wallets. This is because they store Bitcoins on a physical piece of equipment that is often plugged into a PC through the USB port.
They are immune to malware attacks and are safer from hackers than other wallets. However, they come at a higher cost since a standard hardware wallet costs anywhere between $100 and $200.
Every Bitcoin address has a string of 26-35 alphanumeric characters known as wallet addresses. A Bitcoin address can be used to transfer BTC to another address on the network, as long as the sender’s wallet software is compatible with that address type.
There are different Bitcoin wallet address formats depending on the wallet software you choose.

Golden Bitcoin Coin
If you have been researching online about Bitcoin, or you are an enthusiastic Bitcoin investor, you have probably come across the Bitcoin golden coin.
Well, what you need to know is that these coins are not worth anything. They are just a trick used by souvenir sellers to make money from unsuspecting investors.
The golden Bitcoin coins are made from metal or plastic and don’t have any real gold on them. In fact, you can buy them online for $1-$2! These coins have nothing to do with Bitcoin and are not related in any way to Bitcoin forks such as Bitcoin Gold or Bitcoin Cash.

What Does a Bitcoin ATM Look Like?
Just like traditional ATMs, a Bitcoin ATM is a portal in which users can engage in a financial transaction. The main difference between traditional and Bitcoin ATMs is that the former users to deposit and withdraw cash, while the former allows users to buy and sell Bitcoin with cash.
The Bitcoin ATM is comprised of a monitor, bill acceptor, QR Scanner, and dispenser. On the backend, these components are integrated by software to make Bitcoin trading easy, fast, and secure.
Unlike traditional ATMs, Bitcoin ATMs are not connected to a bank account. Rather, they are connected to a cryptocurrency exchange via the web. These exchanges allow users to sell and buy BTC instantly.
The first Bitcoin ATM was erected in 2013 at the Waves Coffee Shop in Vancouver, Canada. Even though it has since been removed, this is the ATM that paved the way for other Bitcoin ATM companies to innovate revolutionary machines that are in use today.

What Does a Bitcoin File Look Like?
Each Bitcoin is a computer file that is stored in a digital wallet on a computer or mobile device. You can send Bitcoins or part of one to your wallet, or you can send them to others.
However, it’s worth noting that Bitcoins don’t exist as individual files. Instead, they are stored as amounts in a Bitcoin address.
The size of the Bitcoin blockchain is 15,000 MB, but you don’t need to download the blockchain to trade or accept Bitcoin.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin is the most popular cryptocurrency in the world and ranks #1 by market cap.
- The 50 Bitcoins in the Genesis Block cannot be spent. The reason behind this is yet to be known.
- Bitcoin golden coins are worthless, and you shouldn’t buy them as a form of investment. Bitcoin only exists online!
Conclusion
What do Bitcoins look like? Well, Bitcoin is a crypto powered by blockchain technology that is not easy to comprehend.
Its claim to popularity is that it is the first decentralized digital currency in the world, meaning that it works without the oversight of a central authority.
Advocates strongly believe that it has the potential to revolutionize the financial space, while critics argue that it’s just a fleeting fad.
Despite the beliefs peddled by skeptics, this cryptocurrency has gained traction across the globe, and companies have now adopted it as an acceptable form of payment.
With the world moving towards a cashless future, Bitcoin could, without a doubt, take its place as the ultimate alternative to traditional currency.
When that happens, be ready. Download Tezro app, where you can exchange currency on a fully encrypted service.